Aiming at low power consumption, Wi Fi 6 continues to expand the mass market!
The new Wi Fi 6 standard (IEEE 802.11) is rapidly becoming a major driver of the wireless local area network (WLAN) market. According to IDC's market research analysts, Wi Fi 6 supported independent access points (APS) accounted for 11.8% of shipments but 21.8% of revenue in the first quarter of 2020. The previous generation of 802.11ac standards still accounted for the majority of shipments (80.9%) and revenue (76.2%).
This is reflected in the recent release of a number of embedded solutions related to Wi Fi 6. Recently, imaging technologies announced that its latest low-power and battery powered applications provide integrated RF and baseband to meet the needs of the Internet of things, wearable devices and audible devices. NXP has also recently announced that it will expand its Wi Fi 6 portfolio to a wider range of market applications based on existing solutions, mainly for high-end products.
Imaging low power Wi Fi 6
Imaging's new iew400, currently licensed, includes integrated RF, AFE, baseband phy and MAC. Its products include integrated RF, AFE, baseband phy and MAC. It is hard core and can be used to simulate and synthesize RTL. Digitalization makes it flexible and fast to market, while reducing development costs.
"The emergence of IOT centric Wi Fi 6 IP and chipsets can more effectively and reliably address the needs of wearable, smart home, industrial and other Internet of things markets, representing an important milestone in the realization of the next generation of low-power Wi Fi," said Andrew zigani, chief analyst of ABI research Solutions like the iew400 will become increasingly important in providing longer life for these devices, improving reliability and robustness, and enhancing performance in dense deployment scenarios. "
Imaging technologies said Wi Fi has witnessed a strong growth in battery powered applications, driven by the widespread use of low-power IEEE 802.11n devices. IEEE 802.11ax enables these products to integrate improved power and efficiency, improve reliability and robustness, and improve performance in dense deployment scenarios.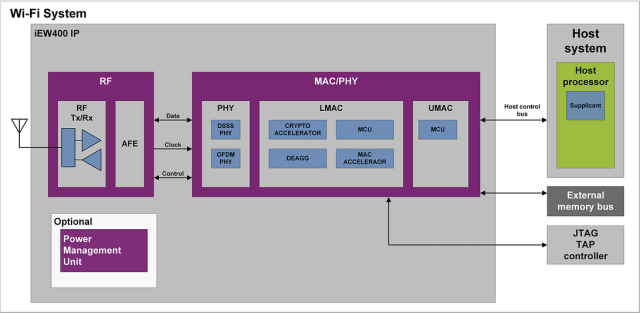
Imagine says its iew400 Wi-Fi 6 IP makes it easy for any microcontroller company to connect to a MCU.
Wi Fi provides some low-power connection solutions that other Bluetooth can't provide, and brings many benefits at the same time. First, there is the potential for more data rates: it can reach 230 Mbps. Wi Fi also has a wider coverage than its competitors, and its operating frequency is 5GHz, much less than the congestion frequency of 2.4GHz. Finally, it also supports IP networks, which is important if you want to send data to the cloud without complexity.
In order to solve the problem of higher power consumption than other alternatives, the key of Wi Fi 6 is to add some new functions. Its design improves data throughput, enhances robustness and reduces power consumption. Imaging hopes that Wi Fi can become the preferred technology for low-power Internet of things applications. Iew400 makes it easy for any microcontroller company to enter the field of connecting MCU. It can also use Wi Fi 6 + ble V5.2 combination IC with Bluetooth low energy (ble) solution.
The efficiency of iew400 is realized by target waiting time (TWT), which is a new Wi Fi 6 function. Access points can negotiate with additional devices when they should be awakened to transmit data. This scheduling means that the device can extend the duration of deep sleep, significantly reduce current consumption and significantly improve battery life. This also means that sensors can effectively collect data for many years at a time outdoors.
In addition, orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) improves the performance in high-density environments. By dividing the bandwidth within the channel, multiple devices can receive data in the same time frame. This ingenious use of bandwidth improves data transmission efficiency, reduces power consumption and significantly improves data throughput.
Two other key features of Wi Fi 6 are BSS coloring and DCM. In BSS coloring, data from each access point is designated as a color, so that clients can identify which access point is being transmitted, thus improving network performance. This solves the problem in areas where there are multiple access points and many customers, such as a large number of people, where Wi Fi is usually difficult to provide consistent throughput because data from different access points may overlap, leading to competition and interference. DCM mode is to modulate the same information on a pair of subcarriers, which can ensure the data to pass through in challenging scenarios.
Imaging Wi Fi 6 IP supports a 2.4/5ghz low-power Wi Fi solution, designed in silicon, with a 6.84 mm2 mode area, including an analog pad, in a TSMC 40nm LP. It includes internal power amplifier, LNA and switch, sleep controller to ensure overall system level power reduction, and optional integrated power management unit (PMU).
NXP's expanded portfolio brings Wi Fi 6 to a broader market
At the same time, NXP recently launched a new Wi Fi 6 product portfolio, which NXP says has IEEE 802.11 features and can be used in a broader market. Mark montierth, vice president and general manager of NXP, said Wi Fi 6 was too expensive to implement at the moment. The new product portfolio will accelerate the large-scale application of Wi Fi 6 in the Internet of things, automotive, access and industrial markets.
"So far, the use of Wi Fi 6 has been driven mainly by smartphones," commented zigani of ABI research. However, we expect that in 2020 and beyond, the construction of the Internet of things, infrastructure and the automotive market will have a huge driving force. This growth will be further driven by power and cost optimized chipsets, such as NXP's latest product, which will increase the viability of Wi Fi in other applications and help open up all new opportunities for this technology. "
NXP's expanded Wi Fi 6 portfolio represents a new vision for end-to-end products deployed on a large scale in multiple markets, with performance including up to 4x performance improvement, wider range, longer battery life and better connectivity reliability.
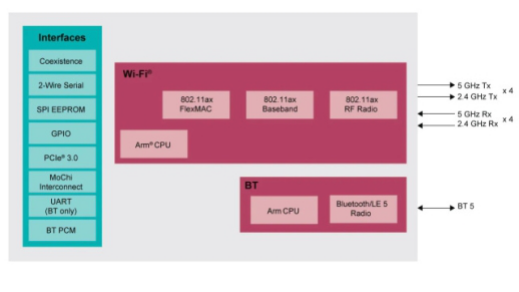
The new combination includes 4 × 4 and 8 × 8 stream solutions, integrating Bluetooth 5 solutions for home and enterprise (88w9064, 88w9068); concurrent dual Wi Fi 2 × 2 and 2 × 2 + Bluetooth 5 aec-q100 qualified solution, designed for the highest performance infotainment and in vehicle information processing applications (88q9098); concurrent dual Wi Fi 2 * 2 and 2 * 2 + Bluetooth 5 solution, and can provide first-class multimedia streaming media and consumer access applications (88w9098); combined with IOT 2 × 2 WiFi 6 + Bluetooth 5 optimization cost and power.
88q9098 automotive Wireless SoC series is the industry's first Wi Fi 6 solution based on the latest IEEE 802.11ax standard. It supports 2x2 + 2x2 concurrent dual Wi Fi, dual-mode Bluetooth 5 / ble and 802.11p networked vehicles.
NXP's innovative concurrent dual Wi Fi architecture is the biggest highlight of 88q9098. This technology integrates two complete Wi Fi subsystems into a single SOC, and enables two independent 2x2 data streams to run in parallel or at full throughput.
In addition, NXP also has a combination of RF front-end (RFFE) solutions designed for MI 105 g smart phones based on SiGe, which can extend Wi Fi 6 functions from low-end to high-end applications, including 1 × 1, 2 × 2, 4 × 4 and 8 × 8 MIMO (multiple input, multi output) solutions, and packaged in Ultra Compact 3 mm x 4 mm modules optimized for mobile devices. It has Wi Fi 6 capabilities, supports advanced portable computing devices, including Premier 5g smartphones, and enables 2 × 2 MIMO with the highest performance.
Extended reading -- basic service set BSS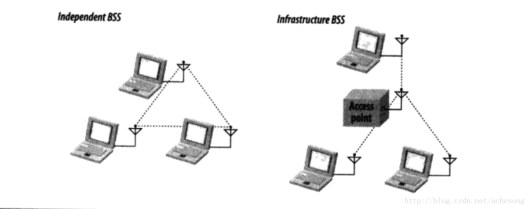
There are two types: independent network and infrastructure network
In the independent basic service set, workstations can communicate with each other directly, but the distance between them must be within the range of direct communication. Usually, the independent basic service set is a temporary network composed of a few workstations for a specific purpose. It is often used in the conference room to support individual meetings. When the conference ends, it collapses. Because of its short duration, small scale and special purpose, it is sometimes called ad hoc BSS or ad hoc network.
Infrastructure based network
On the right side of the above figure is infrastructure BSS. To determine whether it is an infrastructure type network, just check whether there are access points involved. The access point is responsible for all communication of infrastructure network, including communication between the same mobile node. If it is necessary for a mobile workstation located in the infrastructure type basic service concentration to communicate with other mobile workstations, it must go through two steps. First, the frame is passed to the access point by the workstation of the initial conversation. Secondly, the access point transmits the frame to the destination. In the infrastructure network, the workstation must establish an association before the access point to obtain network services. The so-called association refers to the process that a mobile workstation joins an 802.11 network.




